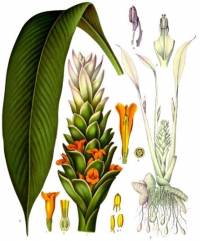
Turmeric is native to the monsoon forests of south east Asia. It is a perennial herb to 1m tall with underground rhizomes. It produces tall, very beautiful, white flower spikes, if clumps are left undisturbed for a year. The flower is so attractive that it is worth growing for this alone. It requires a well-drained soil, frost-free climate and 1000 to 2000mm of rain annually or supplementary irrigation. It thrives best on loamy or alluvial fertile soils and cannot stand waterlogging. Heavy shade will reduce the yield but light shade is beneficial. Ground turmeric comprises 25% of curry powder and is used to give it a yellow colour. The harvested rhizomes are boiled and sun-dried for 7-8 days but can be used fresh. It is also used as a yellow food dye, replacing tetrazine. Leaves wrapped around fish flavour it during cooking. In Indonesia, the young shoots and rhizome tips are eaten raw. Plant turmeric in September or October, into a warm soil. The rhizomes should be planted 5-7 cm deep. It is often planted on ridges, usually about 30-45 cm apart and with 15-30 cm between plants. The crop is planted by setts (small rhizomes) with one or two buds. Approximately 1,700 kg of setts are required to one hectare. Expected yield would be 13 to 35 tonnes/ha of fresh turmeric. In cooler areas of Australia turmeric can be grown in glasshouses. Like all herbaceous perennials clumps of turmeric need to be broken up and fresh pieces planted every 3 to 4 years. Rhizomes are harvested 9 to 10 months after planting, the lower leaves turning yellow or stems drying and falling over are indications of maturity. It is possible for the home gardener to just dig carefully at the side of a clump and remove rhizomes as needed rather than harvesting the whole clump.